例:渡辺皮膚科・形成外科クリニック 副院長
渡辺朋美 先生
For health-conscious middle-aged and older adults, “stroke” is one of the major concerns. Especially in the case of “ischemic stroke,” where a blood vessel blockage leads to brain cell damage, long-term aftereffects may remain. In this context, a study has shown that “antioxidants” may help reduce the damage caused by ischemic stroke.
The study introduced here is titled: “Neuroprotective Effects of a Novel Antioxidant Mixture Twendee X in Mouse Stroke Model.” This research explores how the antioxidant supplement “Twendee X” affects mice with induced stroke.

This paper was published in the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases (J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis), an internationally renowned journal dedicated to cutting-edge stroke and cerebrovascular disease research.
It covers topics such as ischemic stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), and plays a vital role in helping physicians and researchers understand new treatments and mechanisms. As a peer-reviewed journal, its credibility is highly regarded. Research published here often influences clinical practices worldwide.
This means that the neuroprotective effects of Twendee X have been recognized for their scientific value and are gaining global attention.
Our bodies naturally produce substances called “reactive oxygen species (ROS)” every day. While small amounts are harmless, excessive ROS can damage cells, leading to aging and disease. Antioxidants help neutralize this oxidative damage.
During a stroke, the interruption of blood flow causes brain cells to undergo extreme stress, triggering a surge of ROS. This exacerbates inflammation and damage, making antioxidant action a key factor in brain protection.
Researchers divided the stroke-induced mice into four groups:
1. Twendee X for 14 days before surgery and continued after surgery
2. Twendee X for 14 days before surgery, no administration after
3. Placebo (saline) for 14 days and continued after surgery
4. Placebo for 14 days with no post-surgery administration (control group)
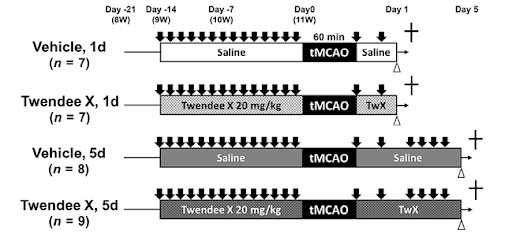
Mouse study design (timing of supplement administration and blood analysis)
The effects of Twendee X were measured using the following methods:
What Are Oxidative Stress Markers?
What Are Inflammatory Markers?
Mice given Twendee X had significantly smaller infarct sizes. The effect was most pronounced in mice that received the supplement before surgery.
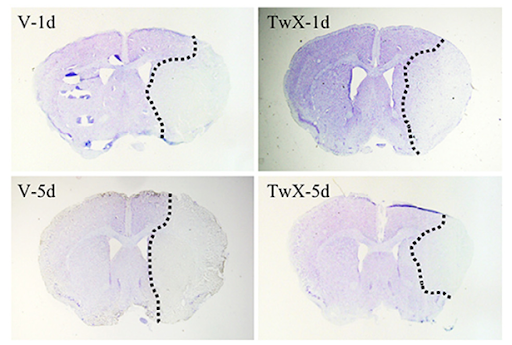
Brain imaging showing infarct areas in control vs. Twendee X-treated mice
Levels of 8-OHdG and 4-HNE—indicators of DNA and lipid oxidation—were greatly reduced in Twendee X-treated mice. This suggests effective ROS suppression.
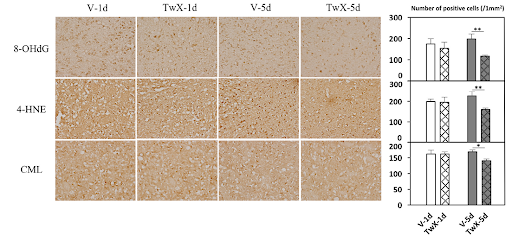
Images and quantification of brain oxidative stress markers (8-OHdG, 4-HNE, CML)
Proteins that promote inflammation (e.g., TNFα, MCP-1) were reduced, indicating that Twendee X helped mitigate secondary brain damage after stroke.
Though this study was conducted on mice, it offers important implications for human health. Twendee X may help prevent stroke-related damage by controlling oxidative stress and inflammation.
However, the study did not specify dosage or usage for humans. For now, the following everyday antioxidant practices are recommended:
The experiment was well-designed, using validated methods. Ingredients in Twendee X, such as vitamin C, CoQ10, and L-cystine, are known antioxidants. Still, human clinical trials are required.
This study suggests that the antioxidant supplement Twendee X may reduce oxidative and inflammatory brain damage in a mouse stroke model.
With further research, it may become a new option for stroke prevention and recovery. Until then, adopting antioxidant-conscious habits—such as a balanced diet and regular exercise—can help protect brain health in everyday life.